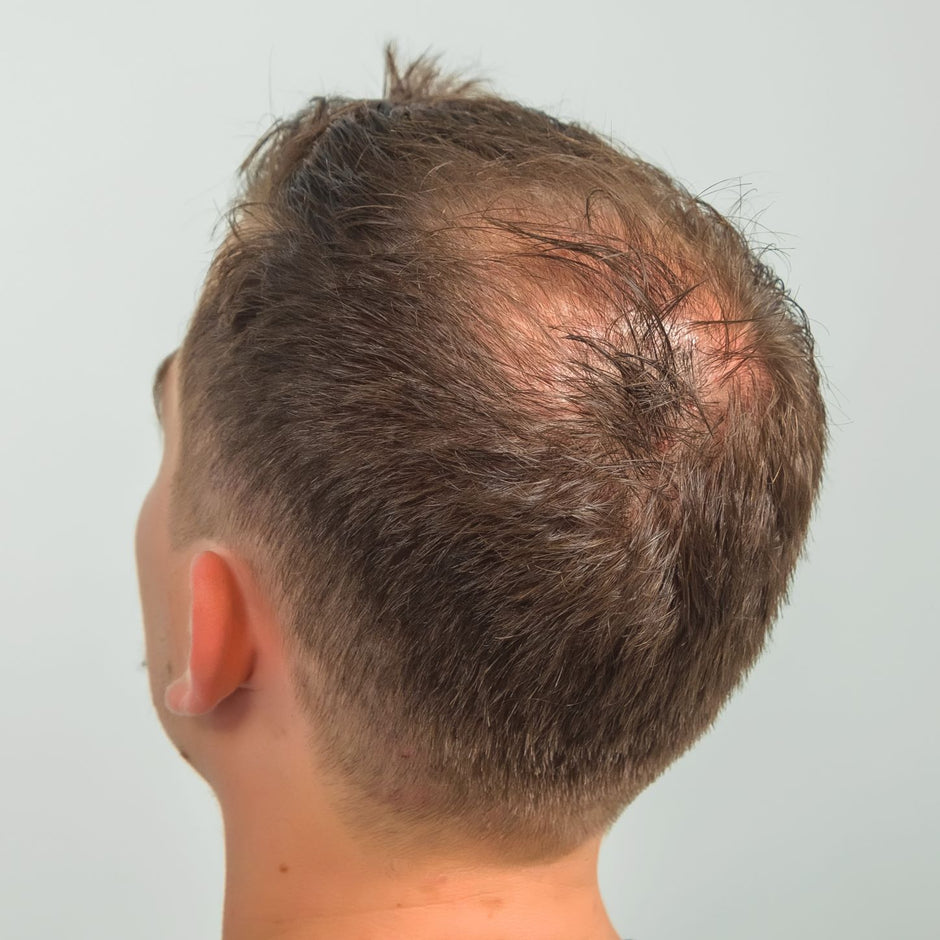
Finasteride is a commonly prescribed medication for male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia), but its effects on hormonal levels are not always fully understood. This article delves into the mechanism of action of Finasteride For Hair Loss Dubai, how it affects hormonal balance, and the potential long-term consequences for users.
What is Finasteride and How Does it Work?
Finasteride is a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor, meaning it works by blocking the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. This enzyme is responsible for converting testosterone, the primary male hormone, into its more potent form, dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is the hormone largely responsible for the shrinkage of hair follicles in individuals with androgenetic alopecia, leading to hair thinning and eventual hair loss.
By inhibiting 5-alpha reductase, finasteride reduces the levels of DHT in the scalp, which helps prevent further hair loss and may even promote hair regrowth in some individuals. However, because DHT plays a role in various physiological processes beyond hair loss, the reduction of this hormone can have systemic effects on hormonal levels.
Impact of Finasteride on Testosterone Levels:
Testosterone is the main male sex hormone and plays a critical role in a wide range of bodily functions, including muscle mass maintenance, libido, and overall energy levels. When finasteride blocks the conversion of testosterone to DHT, it theoretically increases the available amount of testosterone in the bloodstream.
Studies have shown that finasteride does not significantly affect overall testosterone levels in most men. The slight increase in testosterone due to reduced conversion to DHT is typically within the normal range and not enough to cause noticeable physiological changes. However, this small fluctuation can have significant effects on the balance of other hormones in the body.
Changes in DHT Levels:
The most profound effect of finasteride is on DHT levels. Since finasteride inhibits the enzyme responsible for converting testosterone into DHT, DHT levels can drop by up to 70% in the body. This reduction in DHT is essential for stopping hair loss, as DHT binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles, causing them to shrink and eventually stop producing hair.
While this reduction is generally beneficial for hair retention, it can lead to some unwanted side effects due to the crucial role that DHT plays in other bodily functions. DHT is involved in the development of male secondary sexual characteristics, such as facial and body hair, as well as the maintenance of prostate health.
Effects on Sexual Health:
One of the most discussed side effects of finasteride relates to its impact on sexual health. Since DHT is involved in the normal functioning of sexual organs, a reduction in its levels can sometimes cause sexual side effects. These may include:
- Decreased Libido: A reduction in DHT can lead to a diminished sex drive in some users, as DHT is thought to play a role in stimulating sexual desire.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Some men report difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection while on finasteride, although this side effect is not universally experienced.
- Reduced Ejaculate Volume: Lower DHT levels may also affect semen production, leading to a decrease in the volume of ejaculate.
It’s important to note that while these side effects are reported by some users, they are not universal, and many men tolerate finasteride without experiencing significant changes in sexual function. In some cases, these side effects are temporary and resolve after discontinuing the medication.
Impact on Prostate Health:
DHT plays a vital role in the health of the prostate. It is involved in the growth and development of prostate tissue, and a significant reduction in DHT levels due to finasteride can have implications for prostate function.
In clinical practice, Finasteride For Hair Loss in Dubai is also used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a condition where the prostate enlarges, leading to urinary problems. By lowering DHT levels, finasteride helps reduce the size of the prostate in men with BPH. However, the same mechanism that makes finasteride effective for BPH can potentially alter prostate function in men without this condition.
There have been concerns that long-term use of finasteride could lead to a reduction in prostate size that might affect prostate health. Some studies suggest that prolonged use of finasteride may slightly reduce the risk of prostate cancer, while others have raised concerns about a potential increase in the risk of high-grade prostate cancer. These concerns remain under investigation, and more research is needed to determine the full implications for prostate health.
Effects on Mood and Mental Health:
Another aspect of hormonal balance that may be affected by finasteride is mood and mental health. DHT is involved in the regulation of mood and cognitive function, and some users of finasteride report experiencing emotional changes such as depression, anxiety, and mood swings.
Although the exact mechanism by which finasteride might impact mood is not fully understood, it is thought that the reduction in DHT levels could influence the brain’s neurosteroid pathways. This may lead to changes in mood, especially in individuals who are genetically predisposed to mental health disorders.
However, the link between finasteride and mental health side effects is still debated. Some studies have shown a connection between finasteride use and mood disturbances, while others have found no significant effects. As with sexual side effects, these mental health issues tend to resolve after discontinuing the medication.
Long-Term Effects of Finasteride on Hormonal Balance:
While finasteride’s effects on DHT and testosterone levels are generally considered mild, its long-term use may lead to subtle hormonal imbalances. For instance, sustained reductions in DHT can potentially interfere with the normal functioning of androgen receptors in the body. This could result in changes in hair growth patterns, skin health, and even muscle mass over time.
Additionally, as the body adapts to the changes in hormone levels, some users may experience ongoing fluctuations in mood, sexual function, or prostate health. The extent to which finasteride’s hormonal effects can have lasting consequences is still a subject of study, and individual responses can vary greatly.
Conclusion:
Finasteride is a highly effective treatment for hair loss, but its impact on hormonal levels should not be underestimated. While it primarily works by reducing DHT, the downstream effects of this reduction can influence a variety of bodily functions. Most users experience minimal side effects, and for many, the benefits of hair retention outweigh the potential risks. However, it is essential for those considering finasteride to be aware of its hormonal impact and discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider. By understanding how finasteride affects hormonal levels, users can make informed decisions about their treatment options.